| |
Synaptic Plasticity in our Daily Communication
A simple
mechanism...
Neurons in our
brain communicate through electro-chemical
signals. Connections between neurons are called
synapses. One basis of learning seems to be that
neurons can influence the probability with which
they receive information from another neuron via
specific synapses:
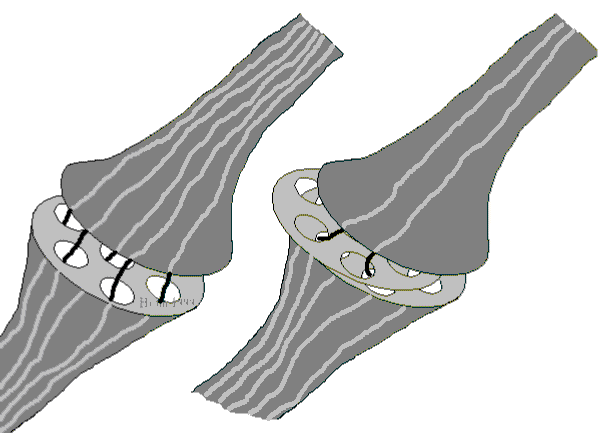
| A synapse is
a variable gap in an information channel.
It can be tuned to either let information
pass almost unhindered, as shown on the
left... |
...or it can
be tuned to make the transit of
information more unlikely, as shown on
the right. |
|
|
|
| |
...common
to our daily intercourse...
If we define people
at work as neurons, any channel of
communication that can be modified in its
likelihood to convey information, can be called a
synapse.
In this sense,
there are already many synapses at work
in our social day-to-day routines:
The
accessability of addresses mirrors the
importance we attach to the people
addressed: Some addresses are pinned on a
table within vision of our desk. These
are most important and used all the time.
Adresses in a small notebook on a shelf
in our bureau come next, followed by
addresses we have in a computer system.
Further down the scale are addresses in
company or public phone-books and last
come those that we don`t have stored
anywhere.
Internet
Browsers offer options to store
"favourite" links, thereby
making them more likely to be used.
In
companies, incoming documents are often
handed from person to person according to
a documented list of priority. The
further up one is on that list, the more
likely one is to receive the information
in time, if at all.
People
considered to be important usually don`t
need to wait just as long in the
ante-chamber of a boss as less important
people.
Colleagues
that one considers to be important for
ones work are more likely to be at ones
dinner table than people considered to be
less important.
The
secretariat of a boss is a synapse par
excellence. She envelops her boss with a
perfect system of weighted informatin
flow: which information should reach his
attention when, how long and in what
circumstances.
The invitation list of
company festivities is often arranged
according to the importance attached to
the invited people, thereby modulating
the likelihood with which information can
flow between them.
More important,
colleagues are usually equipped with
better and time-saving communication
tools (faster computers, better telephone
systems, a secretariat of their own
etc.), thereby giving them the chance to
handle more information per time, thus
exercising more influence.
Defunct communication
channels are usually repaired in
accordance to a persons importance. A
young trainee with no special duties will
probably wait longer for his telephone to
be repaired than a senior manager
involved in production.
|
|
| |
...could be
supported by communication software,...
Any device that
can modify the chance of communication between
two network participants can be called
"synaptic". The ability to filter and
order information gains in effect as information
is supplied in superabundance.
Internet
Browsers and other programmes already try
to figure out which information a certain
user might want at a given time. Entering
some search word in a search engine, the
browser, on its own accord, offers
relevant advertisments or background
information on the spot.
Continuous
"personlization" of a users
information gathering habits reflect a
users temporary preferences and therey
quite explicetly the importance he
attaches to certain sources of
information.
Incoming
E-mails could be listed in order of the
importance attached to the content.
Importance could be inferred by the name
of the sender, the project mentioned in
the title, the date the mail was sent,
the number of recipients, key-words found
in its content or, preferably, any
combination of these. Internet
search-engines might provide good hints
at good mechanisms as they, too, have to
asssess the relevance of perhaps 200.000
pages found as a result of a certain
search request.
|
|
| |
...might
enhance some rudimentary neural intelligence of
company communication networks and...
Memory and learning in brains are
usually seen in close conjunction with the
formation and alteration of synapses.
Imagine a toddlers brain wants to recognize its
mother. Its neural network has already
many subroutines at hand that might help: the
visual recognition of dark lines, of round
objects, of uniform patterns, of star-like
shapes, the auditory recognition of certain tones
of voice, perhaps of word fragments, too, the
olfactory recognition of oily, sweaty or perfumed
smells. Which of these possible key-senses should
be used to identify the mother? The most
successful combination of these will be the best
answer. If the toddlers project is to identify
its mother, the synapses should be so tuned as to
bring exactly those subroutines into close
communication that are the best team to do the
trick.
Equally so in business life. Imagine
a company wants to recognize its best market.
The best answer will be produced if the right
people and the right departments will have their
optimum share in shaping the decision.
Communication synapses would help in determining,
for example, how often and at what times
controlling or production planning departments
could spawn their information and points of views
on other company neurons. If experience shows,
that production planning does not contribute
effectively to a specific question, then the
synapses around this department should lower the
likelihood with which production planning
information and views are transmitted to other
departments and people. This would clearly be one
step towards a learning company structure.
|
|
| |
| |
...refines
the model of the neuron.
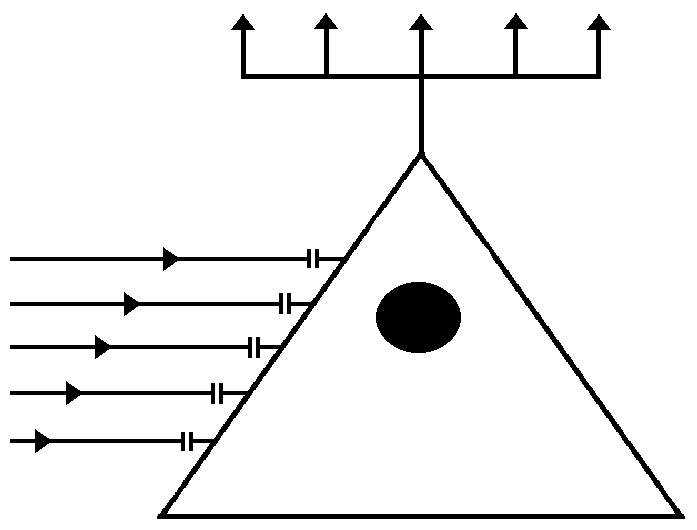
The ingoing
information of a neuron must pass synapses, which
are represented as double-bars. How the synapses
are tuned to let information pass or not, is a
matter of further refinement of the model.
|
|
|

